Forced breathing involves active inspiratory and expiratory movements. During forced breathing, the accessory muscles assist with inhalation. Exhalation involves contraction of the internal intercostal muscles. The abdominal muscles are involved during the maximum levels of forced breathing. Contraction of the abdominal muscles compresses the abdominal contents, pushing them up against the diaphragm and further reducing the volume of the thoracic cavity. Inhalation during quiet breathing involves contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostals muscles, but exhalation is a passive process.
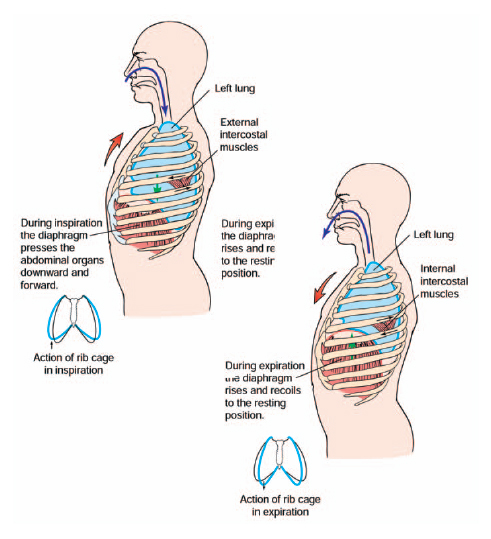
Respiration and inspiration. (From Weber, J., R.N., Ed.D., and Kelley, J., R.N., Ph.D., Health Assessment in Nursing. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 2003.)

